Iron Bank v1
EDB Postgres for Kubernetes(PG4K) is available on Iron Bank. As you can read in the overview page:
Iron Bank is the DoD's source for hardened containers.
[… snipped …]
Iron Bank ultimately is for anyone to consume or contribute. However, we specifically target the following personas:
- DoD organizations wishing to consume hardened containers and Iron Banks BoE (Body of Evidence) for each container
- DoD organizations wishing to help contribute to containers (e.g. bug fixes, new applications, updates)
- DoD Authorization Officials wishing to understand the risks associated with applications
- Commercial vendors wishing to bring their application to the DoD
Iron Bank is a part of DoD's Platform One.
You will need your Iron Bank credentials to access the Iron Bank page for EDB Postgres for Kubernetes.
Pulling the EDB PG4K image from Iron Bank
The images are pulled from the separate Iron Bank container registry. To be able to pull images from the Iron Bank registry, please follow the instructions from Iron Bank.
Specifically, you will need to use your registry1 credentials to pull images.
To find the desired operator image, we recommend to use the search tool to look
with the string edb, and filter by Tags, looking for stable, as shown in
the image. From there, you can get the instruction to pull the image, for
example using Docker:
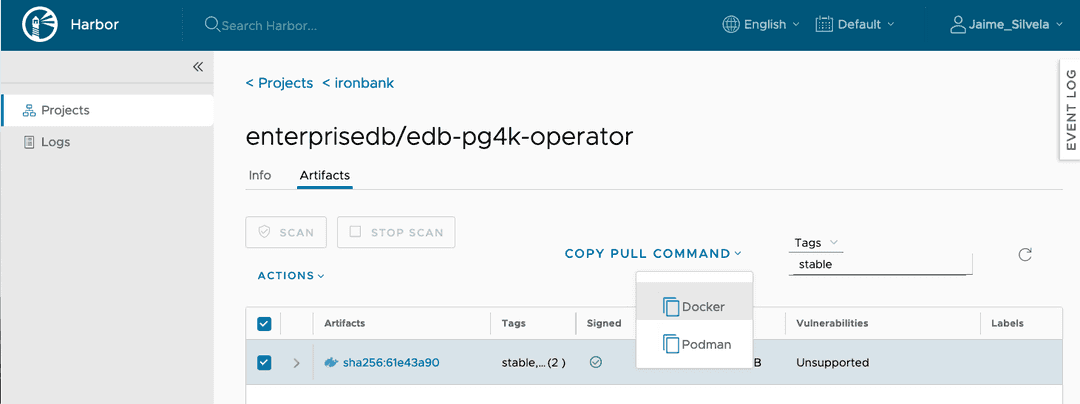
Installing the PG4K operator using the Iron Bank image
For installation, you will need a deployment manifest that points to your Iron
Bank image.
You can take the deployment manifest from the
installation instructions for EDB PG4K.
For example, for the 1.22.0 release, the manifest is available at
https://get.enterprisedb.io/cnp/postgresql-operator-1.22.0.yaml. \
There are a couple of places where you will need to set the image path for the
IronBank image.
apiVersion: apps/v1 kind: Deployment metadata: labels: app.kubernetes.io/name: cloud-native-postgresql name: postgresql-operator-controller-manager namespace: postgresql-operator-system spec: [… snipped …] template: metadata: labels: app.kubernetes.io/name: cloud-native-postgresql spec: containers: - args: - controller [… snipped …] env: - name: PULL_SECRET_NAME value: postgresql-operator-pull-secret - name: OPERATOR_IMAGE_NAME value: <INSERT-YOUR-OPERATOR-IMAGE> [… snipped …] image: <INSERT-YOUR-OPERATOR-IMAGE>
If you wish for the operator to be deployed from Iron Bank directly, you will need to create and set the pull secret with the credentials to the registry, as described above.
It may be easier to get the image from Iron Bank with the instructions on the site, and from there, re-tag and publish it to a local registry, or push it directly to your Kubernetes nodes.
Once you have this in place, you can apply your manifest normally with
kubectl apply -f, as described in the installation instructions.